How to translate a website properly Explained in 7 steps

Having a translation of your company’s website or e-commerce is increasingly important in today’s globalised world. It allows you to reach a wider audience, offer a better user experience, increase sales and generate greater trust. But it all boils down to increasing turnover, which is what companies really want in the long term. If you have got as far as this post, then you probably already know about all of this and what you want to know is how best to translate a website. That is what we are here to explain.
What are the implications of translating a website?
Unless you have a tailor-made content manager – which only big companies have – your website was most likely designed using WordPress, Shopify, Magento, Joomla or Drupal. As these are the most popular content management systems, they offer several tools (such as plug-ins and add-ons) which make translating a website into different languages easy. In the next section we will list the main ones.
However, translating a website is not just about converting text from one language into another; it requires a strategic outlook to guarantee contents (and your own products and services) make sense in every language. They must also be optimised for search engines such as Google, and you must also be ready to serve customers who speak other languages. Finally, you also need a marketing plan which effectively attracts users from the market you are targeting with your translation.
Knowing which market to target
Therefore, you must first ask yourself whether it is the right time to translate your website and what languages to translate it into. One way to answer that question is checking whether your website is already receiving international visitors. You can easily find out using Google Analytics, by checking what browser language settings visitors to your website use (this is better than looking up their location, since they may live in the same place but speak a different language).
You can find this information under Reports > Audience > Geo > Language. If you already have international visitors interested in products and services which are not available in their language, a translation of your website to that language is likely to be well received. On the other hand, if your visitors mostly speak the language the website is currently in, you will need to use other methods to find out what your website’s international potential is. If you also operate offline and already have international customers, that will be a good indicator. Otherwise, you will need to conduct thorough research into the market for your products and services in each country.
Knowing how to address that market
A version of your website in a different language needn’t be a copy of the original. You may not be interested in offering exactly the same products or services in a different market, due to the costs this would entail or because some products may be culturally ill-suited, etc. For example, a company selling premium hampers of local produce may wish to sell this same product in another country. In that case, the company should take into account not all local produce may enjoy the same prestige in the target country and consequently consider modifying the contents of their hamper. It could also be the case that premium hampers were not an established product in the target market, making them harder to sell.
It will therefore be useful to have a marketing team, whether in-house or external, and a specialised translation company which knows your home market and your target market, as well as the terminology related to your business.
Knowing the resources you have
Before making a choice about the technicalities of a translation, you need to know what resources you can count on. These will determine your choices.
- What is your budget? Your budget will make a difference to whether or not you can pay a professional translator, what technology you can use on your website (different software comes at different prices) and whether you should use machine translation software such as Google Translate or Chat GTP. These offer sometimes inaccurate and poor translations which can negatively affect your image and even cause legal problems. You should also bear in mind this budget cannot be a one-off. You will need to update translations every time you upload new content. Otherwise, you might give off an image of carelessness in some markets.
- When do you need it for? Usually, being in a hurry entails a higher cost. This is because more tasks have to be externalised or solved resorting to solutions provided by software, running a greater risk of ending up with inaccuracies or poorly-written texts. You should also take into account the time it will take to update new content in every language you translate to.
- How important is it to have accurate and well-written texts? Some may believe this is only important for big companies or certain sectors where a badly-used term could incur legal liabilities. Yet language is the main way people communicate. It is how we express our ideas and needs in any business. That is why disregarding it can lead to not only missing business internationalisation goals but also economic losses. Therefore, accurate and well-written texts should always be held as important, even if it is up to the company to decide how far to make it a priority.
What options do you have when translating a website?
Once you have thought through the questions above, we are ready to have a closer look at the tools available:
- Plug-ins and add-ons on WordPress, Shopify, Joomla, etc. his option suits any budget, timeframe and need for accuracy, since it allows you to work with either human or machine translation. There is a variety of price and complexity on offer.
- WPML
- Weglot
- Polylang
- TranslatePress
- Lingotek
- Joomfish
- Mageplaza Language Translator
- Copying and pasting content manually. This option is the most common for those who have a tailor-made website, whether it is because they wrote their own code, they use different websites for each language or they use a content manager developed especially for their company (this usually happens in big companies). It allows you to work with human or machine translation, but it is more time-consuming since it will require somebody to upload content to websites manually and, in many cases, copy them from the source first and then paste them into a translation software.
- Trusting browsers. This means not translating your website at all. Most browsers nowadays offer an in-built translation feature (especially on mobiles, which are the most used devices), which shows an automatic translation of a website. It is a cheap (in fact, free) option which is also instant. The drawback is that the company has no control over their website, leaving the marketing of its products and services in other markets in the hands of users and software.
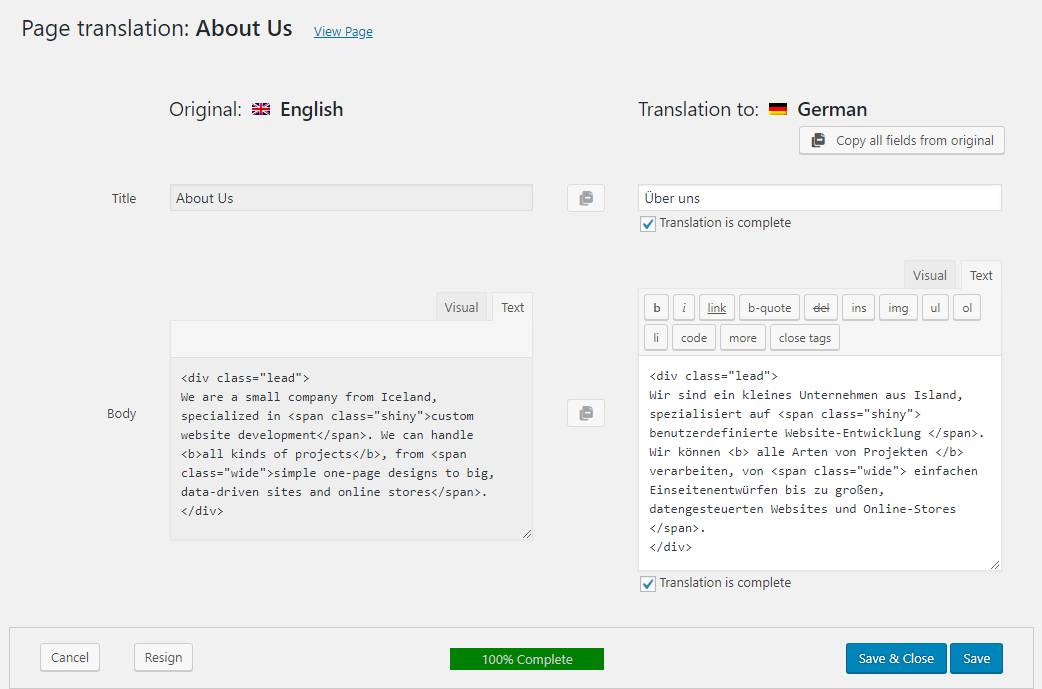
We discuss the most common plug-ins at greater length in this other post.
You should also bear in mind there are two main options when translating texts:
- Machine translation. This is a way to get our texts translated at a low price (or even for free), which can be done either manually (copying and pasting from your website) or automatically, using a plug-in or some other software, which is usually much faster. However, despite the fact that nowadays machine translation has greatly improved both in terminological accuracy and style, since it now uses statistical models and machine learning to offer a cheap and quick translation, the quality and accuracy of the texts it produces leave room for improvement.
- Professional human translation. In this case the translation is made by a human, assisted by translation tools such as glossaries and translation memories. This kind of translation requires a careful analysis of its content, an attentive choice of wording, and an adaptation of the message to nuances in the target language and culture. Moreover, it benefits from the translator’s experience and skill to solve any complex translation problem which may arise.
Steps to translate a website using a plug-in and a professional translation service
There are different ways of translating a website. Using plug-ins or add-ons is one of the most common. Combined with a professional translation company, it is the most appropriate choice for a professional website. Here is how to do it.
1. Installing and setting up the plug-in
The first thing you should do is install the plug-in you have chosen, whether it is free or not. You will need to pick a source and target language, images, contents, menus, etc. This process will depend on the plug-in you chose.
2. Generating and editing the translation
You can then make changes to the translation and add your translation to your website. The way to do this changes with each plug-in, although the overall process is usually fairly similar. This kind of software seeks to be intuitive, easily allowing users to work out how to use it.
3. Using keyword and localised phrases
You want your translated website to be easily found on search engines such as Google or Bing. That is why it is key your translation includes relevant search and localisation terms, in order to guarantee it will appear among the top results for informational or commercial keywords. This includes researching keywords and phrases used by your target market and incorporating them into the translated content. That is why it is important the translators know those keywords and preferred phrases, and approve them.
4. Translating meta tags and URLs
Meta tags, such as titles, descriptions and keywords play a key role in Search Engine Optimisation (SEO). It is therefore essential to translate these tags accurately to guarantee they are true to the website’s content. You should also translate URLs to make sure they contain the relevant keywords and are optimised for Google indexing (depending on the country, you may want to focus on a different search engine).
5. Localising images and multimedia content
Images and multimedia content must be localised to the target language. This includes the translation of captions, ALT tags and file names, since they also affect SEO positioning.
6. Paying attention to the website’s structure
The website’s structure is crucial for both SEO and boosting the conversion rate, i.e. getting visitors to do what you want them to do, whether that is buying, asking for information, subscribing to a service, downloading a service, etc. In order to do this, it is essential to maintain the same structure in the translated website, unless you have deliberately chosen to offer users a completely different website. All of this means URLs, tags and categories should be coherent in all languages.
7. Using hreflang tags
Hreflang tags are used to inform search engines that a website has versions in several languages. This helps search engines such as Google or Bing pick which version to show users. It is therefore essential to add hreflang tags to translated content to guarantee search engines show the version for the correct language.


